05 - Microsoft File Systems and The Windows Registry
Class: CYBR-405
Notes:
Module Objectives
By the end of this module, you should be able to:
- Explain the purpose and structure of file systems
- Describe Microsoft file structures
- Explain the structure of FAT disks
It's the DATA
Understanding File Systems
- File system: Gives OS a road map to data on a disk
- Type of file system an OS uses determines how data is stored on the disk
- When you need to access a suspect's computer to acquire or
- You should be familiar with both the computer's OS and file systems inspect data
Older "Spinning" Disks
Platter, Sector, Track, Cluster
- Hard Disk has a many platter, read and write head and spindle motor.
- Look at: The Memory Hierarchy#What's Inside a Disk Drive?
/CYBR-405/Visual%20Aids/Pasted%20image%2020260211092203.png)
Notes:
- The read and write heads float to barely some nanometers on top of the platter, this is why it was so crucial back in the day to not drove your laptop/hard drive because you could write stuff somewhere accidentally
- You can even break your boot
- If the head makes contact with those platers, those sectors are pretty much toast.
- Inside tracks, they sectors (pie slices) divide this into track sectors
- Cluster is logical data put together
- For one file we could have multiple clusters
- We call this fragmentation
- When you partition your hard drive you can set the number of bytes per sector
- 4K per sector is the default nowadays
SSD Drive (Solid State Drives)
- Have no moving parts
- Full of memory micro chips (flash memory modules)
- Memory cell: Charge trap flash
- Like an excel spreadsheets with 50000 columns and 40000 rows with 100 levels of height
/CYBR-405/Visual%20Aids/Pasted%20image%2020260211093601.png)
Notes:
- Forensics-wise: sometimes there is electron leakage
- Once the device is powered off, those electros can leak at some point
- You better have taken good notes
- You are not going to remember 4 years from now when you go to court
Format a Drive
Common File Systems
- FAT - File Allocation Table (Windows/Universal)
- Very limited in size
- NTFS - New Technology File System (Windows)
- Introduced in Windows NT -> the base for modern windows
- It had a new thing called Journaling
- Used to check the data over
- HFS/HFS+ - Hierarchical File System (Mac)
- HFS+ added journaling
- APFS - Apple Protected File System (Mac)
- Very similar to NTFS but this can be encrypted
- EXT 2/3/4 - Extended File System (Linux)
File System
Master File Table (MFT) stores metadata
- At least 1 entry per file
- File Name
- Size
- Location
- Time Stamps
- Status
- Other information
File System Management
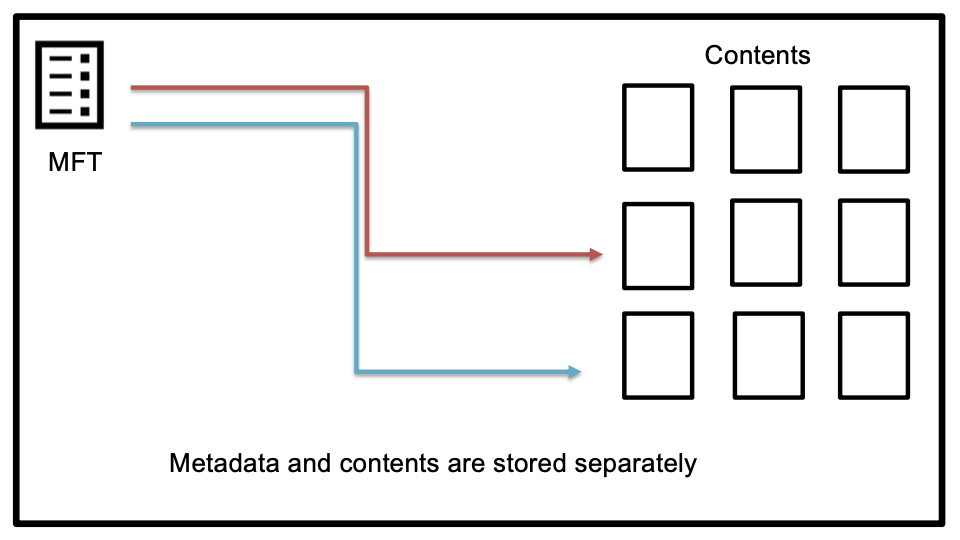
Note:
- Metadata for a file is stored separately from the file, it is in the MFT
Exploring Microsoft File Structures
- In Microsoft file structures, sectors are grouped to form clusters
- Storage allocation units of one or more sectors
- Clusters are numbered sequentially starting at 0 in NTFS
- Depending in the number of sectors
- The OS assigns each cluster a number, called logical addresses
File Fragmentation
- An unintentional side effect of FAT16 allowing large clusters was that it reduced fragmentation as cluster size increased
- When you run out of room for an allocated cluster, the OS allocates another cluster for your file
- As files grow and require more disk space, assigned clusters are chained together
- As some files are created and deleted, the chain can be broken or fragmented
/CYBR-405/Visual%20Aids/Pasted%20image%2020260211095209.png)
Deleting Files
- In Microsoft OSs, when a file is deleted
- Directory entry is marked as a deleted file
- With the HEX E5 character replacing the first letter of the filename
- FAT chain for that file is set to 0
- Data in the file remains on the disk drive
- Area of the disk where the deleted file resides becomes unallocated disk space
- Available to receive new data from newly created files or other files needing more space
/CYBR-405/Visual%20Aids/Pasted%20image%2020260211095431.png)
Notes:
- Most OSs don't actually delete files, they just mark data as deleted
- Just know that the data is still there and there are ways to access it
Slack Space
- Microsoft OSs allocate disk space for files by clusters, resulting in slack space
- File slack - refers to the data between the last byte of the file and the end of the cluster
- Drive slack - refers to clusters that have been unallocated but not overwritten. It can also refer to unallocated space that no longer falls within a partition boundary
/CYBR-405/Visual%20Aids/Pasted%20image%2020260211095632.png)
- Slack Space: unused space in a cluster between the end of an active file’s content and the end of the cluster
Reformat a Drive
- Create date of a MFT corresponds to date it was formatted because the format process creates a new MFT
- File system will only show you what is listed in the current MFT
- What happens to data that was there before?
Forensic tools search for the prior MFT and reconstruct the previous file system or you can file carve.
Data Carving
File Headers\Data Signature - first few bytes of a file.
/CYBR-405/Visual%20Aids/Pasted%20image%2020260211095913.png)
Contents only – no metadata unless its part of the file
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_file_signatures
Disk Partitions
-
Someone who wants to hide data can create hidden partitions between partitions on a disk drive
-
On disk drives with multiple partitions, there are small unused spaces between partitions called the partition gap
-
Data can also be hidden at the end of a disk by declaring a smaller number of bytes than the actual drive size
-
To access a hidden partition or the ending section of a drive, a disk editor can activate the hidden partition by updating the partition table
-
The GUID GPT utility was developed to replace the MBR
- A GPT drive can access up to 18 EB per partition
- GUID = Global Unique Identifier
-
The partition boot sector 0 is the first sector of the first cluster, which consists of one or more sectors of the partition
-
In sector 0 of the boot partition's cluster 0 is information that contains the number of bytes per sector, how many sectors are assigned to a cluster, and the number of sectors allotted to the partition
“The difference between ordinary and extraordinary is that little extra.”
Jimmy Johnson