Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Overview
- XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) vulnerabilities allow an attacker to inject and execute JavaScript on the client-side.
- Also check: XSS and XSRF.
- Similar to HTML Injection, but XSS involves executing code rather than just altering HTML structure.
Potential Impact
- Stealing session cookies
- Hijacking user accounts
- Redirecting users to malicious sites
- Defacing the site
- Executing further client-side attacks
Types of XSS
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Reflected XSS | User input is immediately reflected back in the page (e.g., in search results or error messages). |
| Stored XSS | Malicious input is stored in the backend (e.g., database) and served to users later (e.g., in comments). |
| DOM XSS | JavaScript reads data directly from the DOM and injects it without sanitization. |
Example: DOM XSS on an Unsanitized Input Field
Vulnerable HTML/JS
Refer to the previous example where user input is displayed using innerHTML (on HTML Injection).
XSS Payload
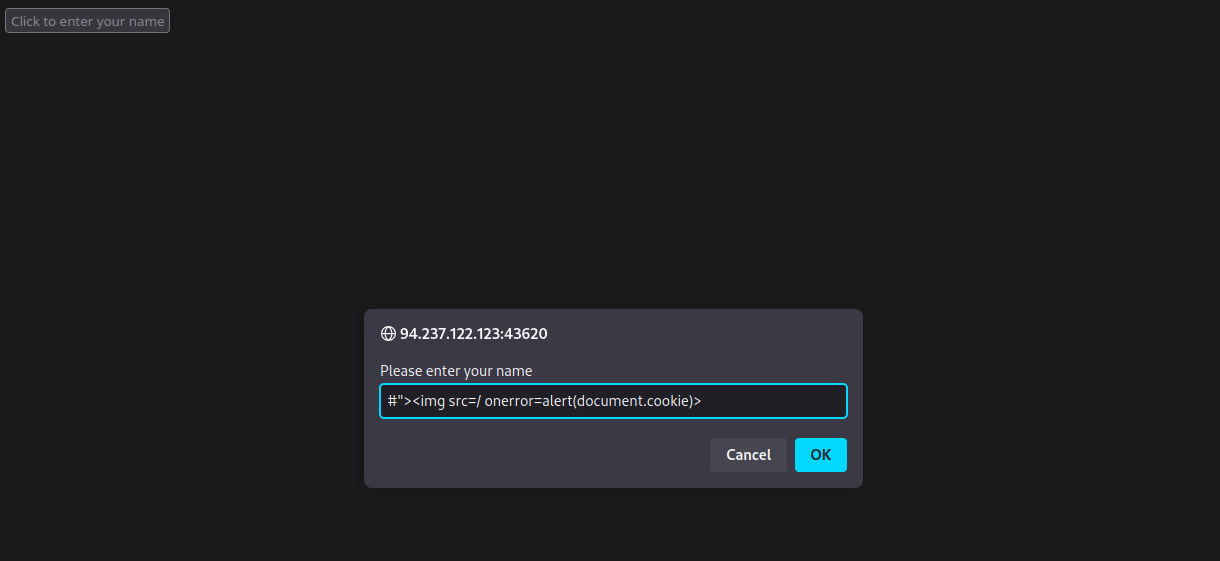
#"><img src=/ onerror=alert(document.cookie)>
Result
- When this payload is entered:
- It creates an invalid image element.
- The
onerrorhandler is triggered. alert(document.cookie)executes, showing a dialog box with the user's cookie.
Visual Outcome
-
A popup appears displaying the user's cookie string.
-
This confirms successful XSS and cookie access.
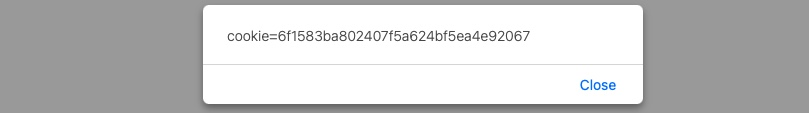
This payload is accessing the HTML document tree and retrieving the cookie object's value. When the browser processes our input, it will be considered a new DOM, and our JavaScript will be executed, displaying the cookie value back to us in a popup.
An attacker can leverage this to steal cookie sessions and send them to themselves and attempt to use the cookie value to authenticate to the victim's account. The same attack can be used to perform various types of other attacks against a web application's users. XSS is a vast topic that will be covered in-depth in later modules.
Security Risks
- An attacker can:
- Steal cookies and impersonate users.
- Modify webpage content or perform phishing.
- Send stolen data to remote servers.
Mitigation Strategies
- Sanitize and encode user input.
- Use safe DOM methods like
.textContentinstead of.innerHTML. - Implement Content Security Policy (CSP).
- Avoid dynamic script execution (
eval(),innerHTML). - Escape characters like
<,>,",', and&.
Note
XSS is a vast and critical topic in web security. It will be explored further in upcoming modules.
Exercise
Target: 94.237.122.123:43620
Try to use XSS to get the cookie value in the above page
Paste the payload from above into the input dialog:
- Click "OK"
You will see the following popup
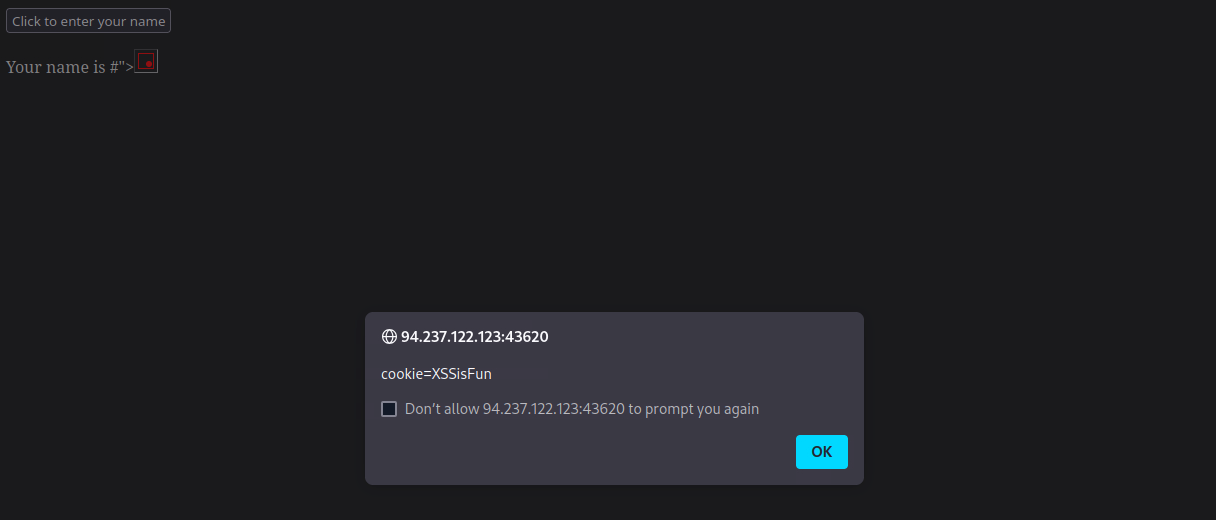
- Copy the cookie value
flag: XSSisFun