Databases
Overview
- Databases store:
- Web app content (posts, updates)
- User data (usernames, passwords)
- Assets (images, files)
- Benefits: quick data retrieval, dynamic content, scalability
Relational Databases (SQL)
- Store data in tables (rows & columns) with relationships between them
- Schema = structure & relationships among tables
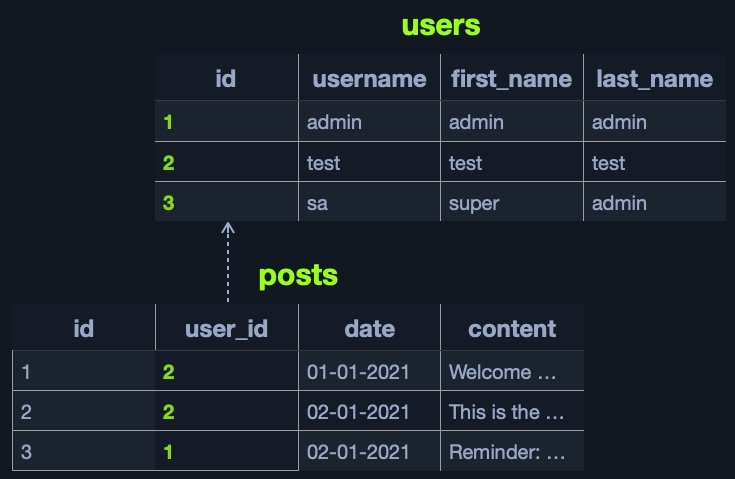
Example Schema
-
Users Table:
id,username,first_name,last_name -
Posts Table:
id,user_id,date,content -
Relationship:
users.id↔posts.user_idExample
Advantages
- Fast and reliable for structured data
- Efficient data retrieval using SQL queries
Common SQL Databases
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| MySQL | Most widely used, open-source, free |
| MSSQL | Microsoft's SQL server for Windows |
| Oracle | Enterprise-grade, highly reliable, expensive |
| PostgreSQL | Open-source, highly extensible |
| Others | SQLite, MariaDB, Amazon Aurora, Azure SQL |
Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL)
- Do not use tables or schemas
- Great for unstructured or semi-structured data
- Highly scalable and flexible
NoSQL Models
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Key-Value | Each item is stored as a key-value pair (JSON, XML) |
| Document-Based | Complex JSON objects with metadata |
| Wide-Column | Data stored in tables with dynamic columns |
| Graph | Nodes and edges representing relationships |
Key-Value Example (JSON)
{
"100001": {
"date": "01-01-2021",
"content": "Welcome to this web application."
},
"100002": {
"date": "02-01-2021",
"content": "This is the first post on this web app."
},
"100003": {
"date": "02-01-2021",
"content": "Reminder: Tomorrow is the ..."
}
}
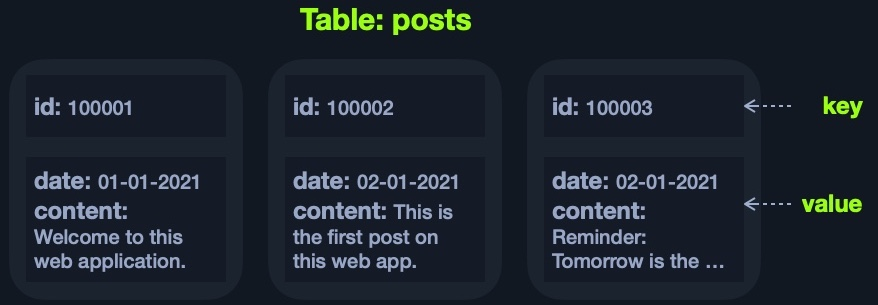
- It looks similar to a dictionary/map/key-value pair in languages like
PythonorPHP'i.e.{'key':'value'}', where thekeyis usually a string, thevaluecan be a string, dictionary, or any class object.
The Document-Based model stores data in complex JSON objects and each object has certain meta-data while storing the rest of the data similarly to the Key-Value model.
Common NoSQL Databases
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| MongoDB | Free and open-source NoSQL database. Most common NoSQL, document-based, JSON storage |
| ElasticSearch | Free and open-source NoSQL database. Fast search engine, handles big datasets |
| Apache Cassandra | Free and open-source NoSQL database. Scalable and resilient |
| Others | Redis, Neo4j, CouchDB, Amazon DynamoDB |
Database Use in Web Applications
PHP Example
For example, within a PHP web application, once MySQL is up and running, we can connect to the database server with:
Connect to DB Server
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "user", "pass");
Then, we can create a new database with:
$sql = "CREATE DATABASE database1";
$conn->query($sql);
After that, we can connect to our new database, and start using the MySQL database through MySQL syntax, right within PHP, as follows:
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "user", "pass", "database1");
$query = "select * from table_1";
$result = $conn->query($query);
Search Input Example
Web applications usually use user-input when retrieving data. For example, when a user uses the search function to search for other users, their search input is passed to the web application, which uses the input to search within the database(s).
$searchInput = $_POST['findUser'];
$query = "select * from users where name like '%$searchInput%'";
$result = $conn->query($query);
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc() ){
echo $row["name"]."<br>";
}
- The web application sends the result back to the user:
- This basic example shows us how easy it is to utilize databases. However, if not securely coded, database code can lead to a variety of issues, like SQL Injection vulnerabilities.
Exercise
What type of database is Google's Firebase Database?
Google Firebase offers primarily NoSQL databases. Specifically, it provides two main options:
- Firebase Realtime Database:
This is a cloud-hosted NoSQL database that stores data as one large JSON tree. It excels at real-time data synchronization, making it suitable for applications requiring instant updates, like chat applications or collaborative tools. - Cloud Firestore:
This is a flexible, scalable NoSQL document database. Data is organized into collections of documents, and documents can contain subcollections. Firestore offers more advanced querying capabilities and better scalability for larger datasets compared to the Realtime Database. It also supports real-time synchronization and offline capabilities.
flag: NoSQL