HTML
HTML Basics and DOM Structure
HTML Overview
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the foundational component of the front end of web applications.
- It defines the structure of web pages using elements like titles, forms, images, etc.
- Browsers interpret and display HTML elements to users.
Example HTML Page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>A Heading</h1>
<p>A Paragraph</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
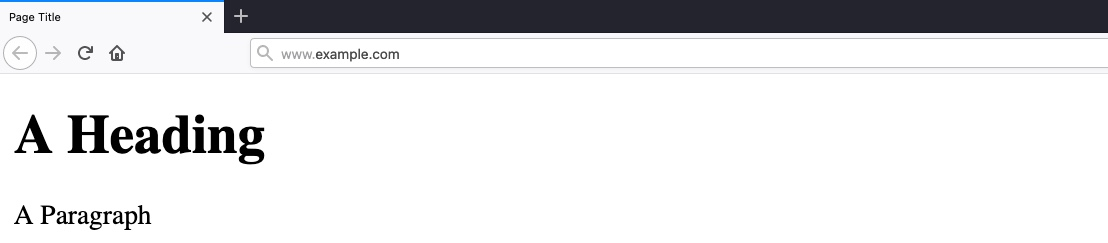
- Page title: "Page Title"
- URL: www.example.com
- Heading: "A Heading"
- Paragraph: "A Paragraph"
HTML Element Tree Structure
document
└── html
├── head
│ └── title
└── body
├── h1
└── p
Each element can contain other HTML elements, while the main HTML tag should contain all other elements within the page, which falls under document, distinguishing between HTML and documents written for other languages, such as XML documents.
HTML Tag Syntax
- Elements open and close with tags:
<tag>content</tag> - Can include
idorclassattributes:- Example:
<p id='para1'>or<p class='red-paragraphs'>- Which is needed for CSS to properly format the element.
- Example:
URL Encoding (Percent-Encoding)
- In URLs, for example, browsers can only use ASCII encoding, which only allows alphanumerical characters and certain special characters.
- Used to represent unsafe ASCII characters in URLs.
- Format:
%followed by two hexadecimal digits.
| Character | Encoding |
|---|---|
| space | %20 |
| ! | %21 |
| " | %22 |
| # | %23 |
| $ | %24 |
| % | %25 |
| & | %26 |
| ' | %27 |
| ( | %28 |
| ) | %29 |
| A full character encoding table can be seen here. |
- Example:
'becomes%27 - Spaces are replaced with
+or%20 - Tools like Burp Suite or online encoders can be used for encoding/decoding.
Important HTML Elements
<head>: Contains metadata like title, styles, and scripts.<body>: Contains the visible content of the page.<style>: Contains CSS.<script>: Contains JavaScript.
Document Object Model (DOM)
- Defined by W3C as a platform-neutral interface for accessing and updating document content and style.
DOM Parts
- Core DOM: For all document types.
- XML DOM: For XML documents.
- HTML DOM: For HTML documents.
Accessing Elements
- Example:
document.head,document.h1 - Enables us to view the source code of a specific element on the page and look for potential issues.
- Elements can be located by:
idtag nameclass name
Usage in Security
- Understanding DOM helps in identifying and manipulating HTML elements.
- Useful for finding vulnerabilities like XSS (Cross-Site Scripting).
Exercise
What is the HTML tag used to show an image?
flag: <img>