Proxying Tools
To route all web requests made by a specific tool through our web proxy tools, we have to set them up as the tool's proxy (i.e. http://127.0.0.1:8080), similarly to what we did with our browsers. Each tool may have a different method for setting its proxy, so we may have to investigate how to do so for each one.
Note: Proxying tools usually slows them down, therefore, only proxy tools when you need to investigate their requests, and not for normal usage.
Proxychains
One very useful tool in Linux is proxychains, which routes all traffic coming from any command-line tool to any proxy we specify. Proxychains adds a proxy to any command-line tool and is hence the simplest and easiest method to route web traffic of command-line tools through our web proxies.
To use proxychains, we first have to edit /etc/proxychains.conf, comment out the final line and add the following line at the end of it:
We should also make use of the -q option, which makes proxychains operate in "quiet" mode, suppressing the output of connection information to the console. (eliminates clutter on screen).
Example:
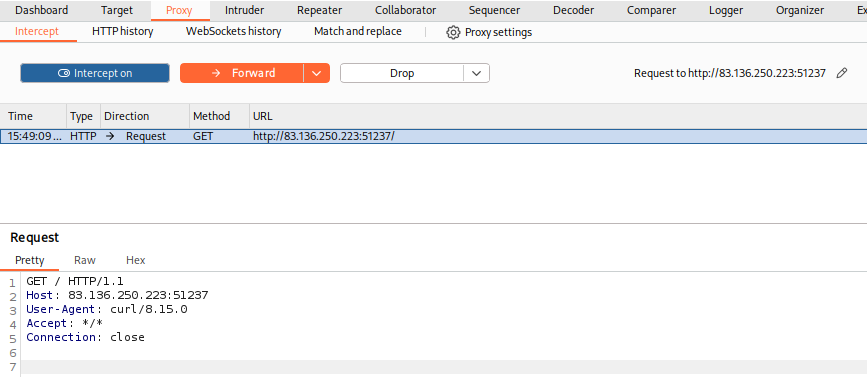
m4cc18@htb[/htb]$ proxychains -q curl http://SERVER_IP:PORT
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Ping IP</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./style.css">
</head>
...SNIP...
</html>
If we go back to our web proxy (Burp in this case), we will see that the request has indeed gone through it:
Metasploit
Finally, let's try to proxy web traffic made by Metasploit modules to better investigate and debug them. We should begin by starting Metasploit with msfconsole. Then, to set a proxy for any exploit within Metasploit, we can use the set PROXIES flag. Let's try the robots_txt scanner as an example and run it against one of our previous exercises:
m4cc18@htb[/htb]$ msfconsole
msf6 > use auxiliary/scanner/http/robots_txt
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/http/robots_txt) > set PROXIES HTTP:127.0.0.1:8080
PROXIES => HTTP:127.0.0.1:8080
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/http/robots_txt) > set RHOST SERVER_IP
RHOST => SERVER_IP
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/http/robots_txt) > set RPORT PORT
RPORT => PORT
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/http/robots_txt) > run
[*] Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
[*] Auxiliary module execution completed
Once again, we can go back to our web proxy tool of choice and examine the proxy history to view all sent requests:
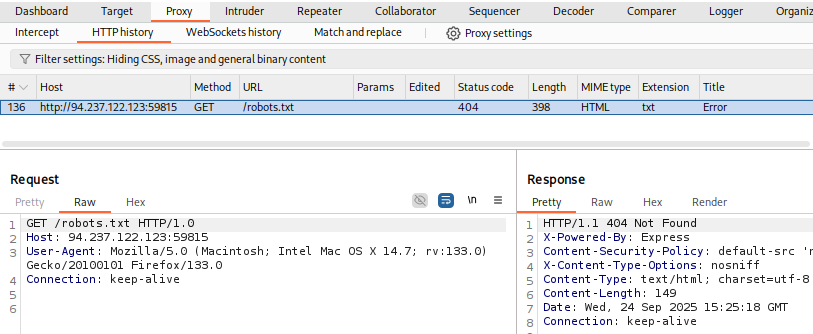
We see that the request has indeed gone through our web proxy. The same method can be used with other scanners, exploits, and other features in Metasploit.
We can similarly use our web proxies with other tools and applications, including scripts and thick clients. All we have to do is set the proxy of each tool to use our web proxy. This allows us to examine exactly what these tools are sending and receiving, and potentially repeat and modify their requests while performing web application penetration testing.
Exercise
Try running 'auxiliary/scanner/http/http_put' in Metasploit on any website, while routing the traffic through Burp. Once you view the requests sent, what is the last line in the request?
Run msfconsole to start Metasploit
msfconsole
msf >
Run the following commands in Metasploit:
msf > auxiliary/scanner/http/http_put
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/http_put) > set PROXIES HTTP:127.0.0.1:8080
PROXIES => HTTP:127.0.0.1:8080
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/http_put) > set RHOST 83.136.250.244
RHOST => 83.136.250.244
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/http_put) > set RPORT 45415
RPORT => 45415
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/http_put) > run
[-] 83.136.250.244: File doesn't seem to exist. The upload probably failed
[*] Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
[*] Auxiliary module execution completed
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/http_put) >
Go to Burp -> Proxy -> HTTP history and look for the request generated by metasploit.
PUT /msf_http_put_test.txt HTTP/1.1
Host: 83.136.250.244:45415
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/131.0.2903.86
Content-Type: text/plain
Content-Length: 13
Connection: keep-alive
msf test file
flag: msf test file