Intro to Databases and types
Intro to Databases
Role of Databases in Web Applications
- Back-end databases store application data such as:
- Core assets: images, files
- Content: posts, updates
- User data: usernames, passwords
- Queries are performed using SQL to interact with this stored data.
Evolution of Databases
- File-based databases: Inefficient with growing data.
- Database Management Systems (DBMS): Introduced for efficient handling and scalability.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
- Software that defines, creates, manages, and interacts with databases.
- Types of DBMS:
- File-based
- Relational DBMS (RDBMS)
- NoSQL
- Graph-based
- Key/Value stores
Ways to Interact with DBMS
- Command-line tools
- Graphical Interfaces (GUIs)
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
Common Uses
- Widely used in finance, banking, education for data management.
Key Features of DBMS
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Concurrency | Manages multiple simultaneous users without data corruption or loss |
| Consistency | Maintains valid and consistent data under concurrent operations |
| Security | Controls access via user authentication and permissions |
| Reliability | Supports data backups and rollback in case of failures |
| SQL Support | Uses SQL with intuitive syntax for data operations |
SQL (Structured Query Language)
- Used to communicate with databases.
- Supports operations: Insert, Select, Update, Delete (CRUD).
Architecture: Two-Tier and Three-Tier
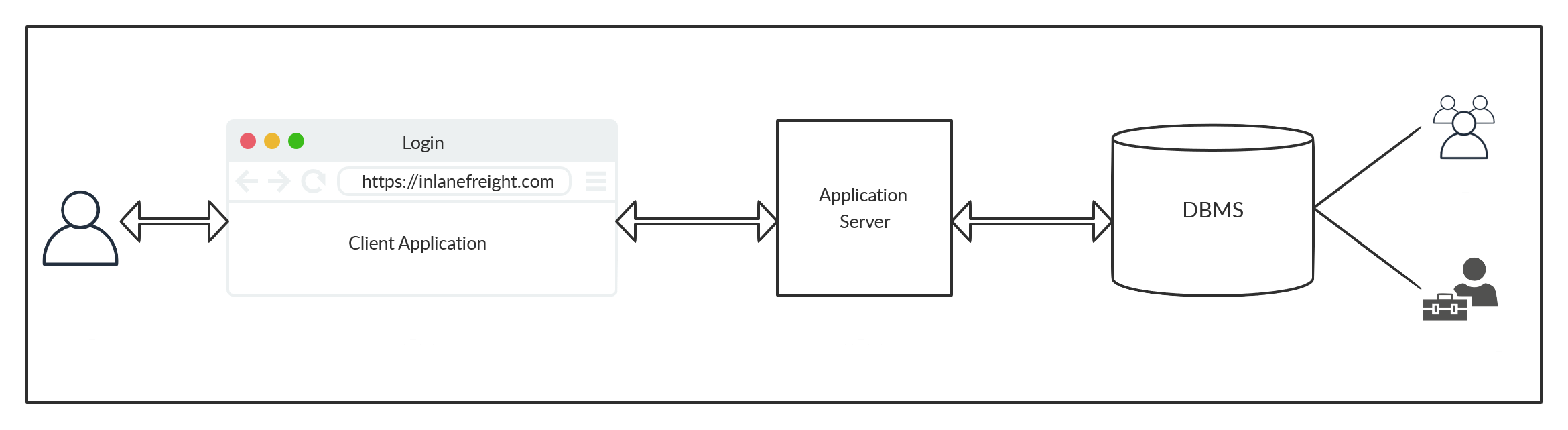
Two-Tier Architecture
- Client ↔ DBMS directly
- Simpler but less scalable
Three-Tier Architecture
- Tier I (Client): GUI/Web interfaces for user interaction (e.g., login, commenting)
- Tier II (Application Server):
- Middleware that translates requests into DB-friendly queries
- Uses DBMS-specific libraries/drivers
- Tier III (DBMS):
- Executes queries: insert, retrieve, delete, update
- Returns data or error codes
Hosting Considerations
- Small systems: Application server and DBMS may share a host.
- Large-scale systems: Separate hosting improves performance and scalability.
Types of Databases
Two Types of Databases
Databases are generally divided into:
- Relational Databases: Use Structured Query Language (SQL).
- Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL): Use other formats and are schema-less.
Relational Databases
- Use a schema (template) to structure stored data.
- Store information in tables (entities) that relate to each other via keys.
Example
-
Customers Table: Stores customer info (name, address, etc.).
-
Products Table: Stores product info.
-
Orders Table: Uses customer and product IDs to track purchases.
-
Primary Keys: Uniquely identify rows in a table.
-
Foreign Keys: Reference primary keys from other tables to establish relationships.
Schema Relationships
- A Schema is the map or structure of how tables relate.
- Efficient for:
- Large datasets with well-defined structure.
- Fast and systematic data retrieval.
Example Table Structure:
userstable:id,username,first_name,last_namepoststable:id,user_id,date,content
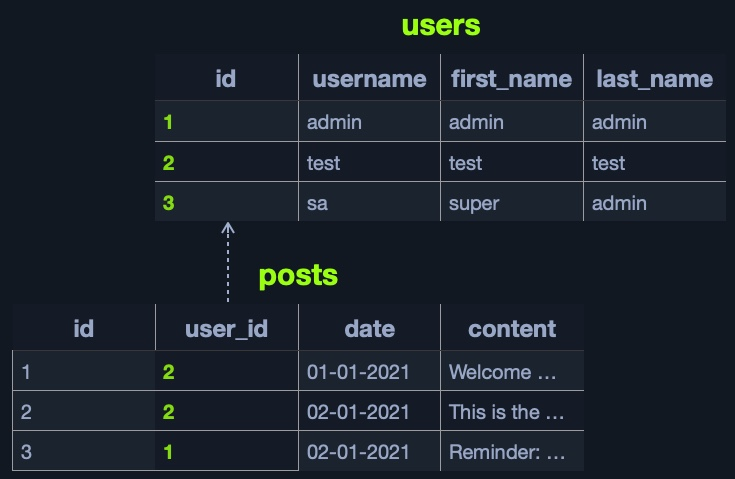
- user_id in
postslinks to id inusers.
Common RDBMS Examples:
- MySQL
- SQL Server
- Oracle
- PostgreSQL
- Microsoft Access
Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL)
- Do not use tables, rows, or strict schemas.
- Best for loosely structured or unstructured data.
- Highly scalable and flexible.
Common Storage Models:
- Key-Value
- Document-Based
- Wide-Column
- Graph-Based
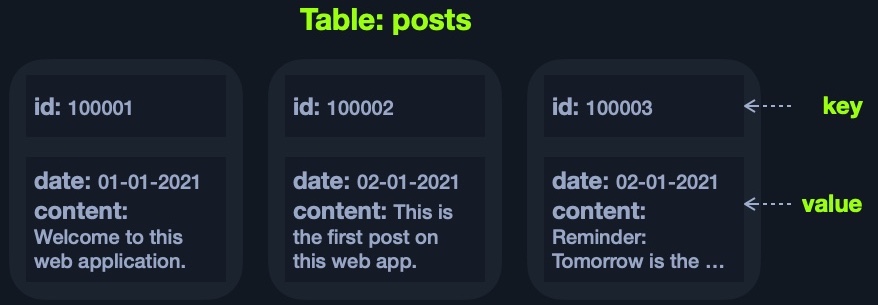
Key-Value Store Example (JSON):
{
"100001": {
"date": "01-01-2021",
"content": "Welcome to this web application."
},
"100002": {
"date": "02-01-2021",
"content": "This is the first post on this web app."
},
"100003": {
"date": "02-01-2021",
"content": "Reminder: Tomorrow is the ..."
}
}
- Similar to dictionary objects in Python or PHP.
- Each key maps to a value (which can itself be a complex object).
Common NoSQL Example:
- MongoDB
Injections
- Relational Databases: Vulnerable to SQL Injection (SQLi).
- Non-Relational Databases: Vulnerable to NoSQL Injection (covered later).